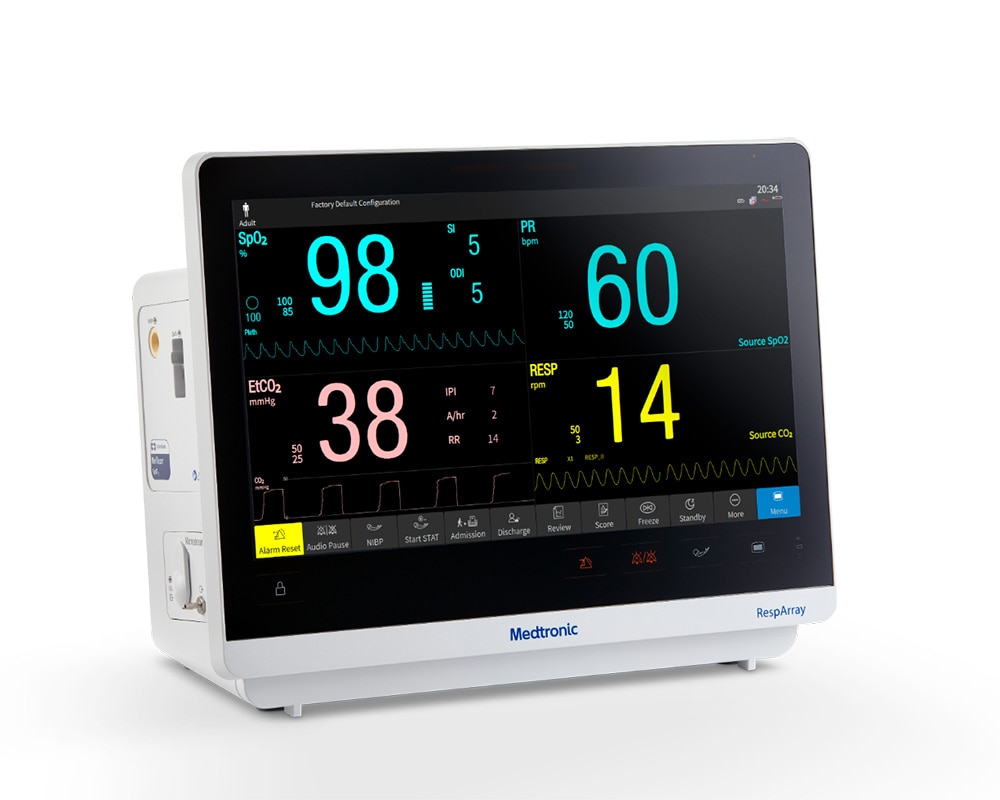
INTUÏTIEVE MULTIPARAMETER PATIËNTBEWAKING
Patiëntveiligheid eenvoudig gemaakt
97%1 van de postoperatieve door opioïden veroorzaakte ademhalingsdepressie is te voorkomen met betere continue bewaking en respons.
Personeelstekort kan het een uitdaging maken om uw patiënten zo vaak te controleren als u zou willen.
Maar wat als u patiënten overal in het ziekenhuis zou kunnen monitoren? Dat kan nu, met de RespArray™ patiëntmonitor.
Hij is ontworpen voor zorggebieden waar steekproefsgewijze controle misschien niet voldoende is, zoals op medisch-chirurgische afdelingen, of waar aanvullende parameters nodig zijn, zoals capnografie bij procedurele sedatie. Het helpt je om ademhalingsproblemen vroeg op te sporen en eerder in te grijpen.2,3,4